Practical Tips for Improving Emotional Intelligence in the Office
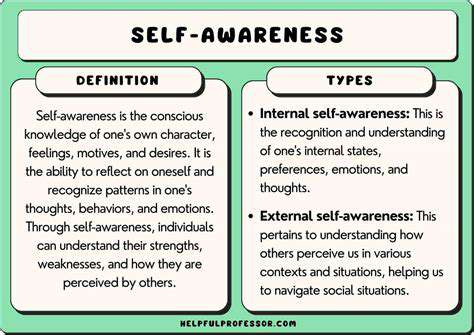
Understanding Self-Awareness and Its Importance
Self-awareness is the ability to recognize and understand one’s emotions, strengths, weaknesses, and values. It is an essential component of emotional intelligence that impacts decision-making and interpersonal relationships.
Studies show that individuals with high self-awareness tend to perform better in professional settings. They not only understand their own emotions but also how those emotions impact their interactions with colleagues and clients.
Techniques to Enhance Self-Awareness
- Regularly practicing reflection to assess emotions and reactions.
- Seeking feedback from peers or mentors to gain external perspectives.
- Keeping a journal to track emotional responses over time.
One effective method for enhancing self-awareness is through regular self-reflection. Carving out time at the end of each day to evaluate how you felt and reacted to situations can unveil patterns in your emotional response. This is not just about recognizing negative emotions; it's also crucial to acknowledge your positive feelings.
Mindfulness Practices for Emotional Clarity
Incorporating mindfulness into your daily routine can significantly improve self-awareness. Mindfulness exercises, such as meditation or deep-breathing techniques, help quiet the mind and allow individuals to focus on their feelings without judgment. Feeling grounded can help you assess your thoughts and emotions clearly.
Research indicates that engaging in mindfulness practices can reduce stress and enhance one's ability to manage emotions effectively. Regular practice can lead to improved emotional regulation and increased resilience, which are important in any workplace environment.
The Role of Feedback in Building Self-Awareness
Feedback from others plays a critical role in developing self-awareness. Colleagues and supervisors can provide insights into behaviors that one may not recognize themselves. Understanding how others perceive you can guide personal development and enhance workplace relationships.
To facilitate constructive feedback, creating a culture of openness and trust is vital. This ensures that individuals feel safe sharing honest observations without fear of negative repercussions. It’s beneficial to ask specific questions about one’s performance and behavior to gain clearer insights.
Setting Personal Goals for Emotional Growth
Setting specific, measurable goals related to emotional intelligence can be a game-changer in fostering self-awareness. These goals could range from improving communication skills to managing stress better during high-pressure situations. Creating a roadmap for these goals enhances accountability.
Regularly reviewing progress towards these goals can illuminate advancements and areas still needing attention. This deliberate tracking encourages continual growth and adaptation, essential aspects of emotional intelligence.
The Impact of Self-Awareness on Team Dynamics
In a team environment, self-awareness can enhance collaboration and understanding among team members. When employees are attuned to their emotions and those of others, they navigate interpersonal challenges more effectively. Teams composed of self-aware individuals tend to exhibit better communication and conflict resolution skills.
According to research, emotionally intelligent teams are more likely to achieve high performance and job satisfaction. This highlights the need for organizations to foster an environment where self-awareness can flourish. Training workshops can be an effective resource in this regard.
Conclusion: Commencing Your Journey Toward Improved Emotional Intelligence
Embarking on the path to enhancing self-awareness is a continuous journey rather than a destination. It requires consistent effort and a genuine desire for self-improvement. Embracing this journey not only amplifies emotional intelligence but can also lead to profound professional and personal growth.
As you begin applying these tips, consider integrating them into your day-to-day interactions. The key is to remain open to learning about yourself and embracing the feedback you receive along the way.
Enhancing Empathy in the Work Environment
Understanding Empathy and Its Role in the Workplace
Empathy involves the ability to understand and share the feelings of others, which is crucial in a work environment where collaboration is often necessary. Research shows that cultivating empathy among team members leads to increased trust and communication, resulting in a more cohesive work atmosphere. In 2019, a study published in the Journal of Business Psychology emphasized that teams with high levels of empathy demonstrate significant improvements in performance and job satisfaction.
Furthermore, developing empathy can significantly impact leadership styles within organizations. Leaders who exhibit empathetic traits often foster a more inclusive culture, enabling all employees to feel valued and heard. According to a survey by Business Solver, 92% of employees believe it's essential for a company to have empathetic leaders, pointing to the importance of empathy in retention and engagement strategies.
Practical Strategies to Enhance Empathy among Colleagues
One effective way to Boost Empathy in the workplace is through active listening exercises. Encouraging employees to practice reflective listening can help them better understand coworkers' perspectives and emotions. This includes paraphrasing what someone has said and responding with acknowledgment before offering solutions or advice. Such techniques not only improve interpersonal communication but also promote an environment of respect and understanding.
Measuring the Impact of Empathy Initiatives
To determine the effectiveness of empathy training programs within organizations, it's essential to establish clear metrics for evaluation. Tools such as employee engagement surveys, 360-degree feedback, and performance appraisals can provide valuable data on how these initiatives are influencing workplace dynamics. A report from Gallup highlighted that organizations with strong empathy practices see a 20% increase in employee engagement and productivity, proving that such initiatives are not merely beneficial but essential for modern workplaces.
Regulating Emotions in Challenging Situations

Understanding Triggers and Emotional Responses
One essential aspect of regulating emotions in challenging situations is recognizing our triggers. Triggers can vary widely from person to person, encompassing everything from workplace deadlines to interpersonal conflicts. Identifying these triggers requires self-reflection and honest evaluation of past experiences that sparked strong emotional reactions.
Research indicates that individuals who maintain an awareness of their emotional triggers are better equipped to manage their responses. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Behavioral Therapy found that participants who employed mindfulness techniques reported a 30% reduction in emotional reactivity during stressful situations. Understanding these dynamics can empower employees to approach challenges more calmly and deliberately.
Strategies for Managing Emotions Effectively
- Practice deep breathing techniques to instill calmness during stressful moments.
- Utilize cognitive reframing to shift perspectives on challenging situations.
- Engage in regular self-assessment to monitor emotional health and fluctuations.
Effective strategies for managing emotions often begin with simple techniques that can be incorporated into daily routines. Practicing deep breathing exercises or grounding techniques can help individuals regain control over their emotional state. For example, taking a few moments to focus on breathing can lower stress hormone levels, facilitating a more constructive response to workplace challenges.
Cognitive reframing is another powerful tool that can reshape your mindset about specific challenges. By consciously changing our perspective, we can transform stressful situations into opportunities for growth. This approach not only enhances emotional regulation but can also boost overall workplace morale. Regularly engaging in self-assessment can keep emotional health in check, allowing for better resilience in the face of adversity.
Building Stronger Relationships through Effective Communication

Understanding Emotional Intelligence in Workplace Communication
Emotional Intelligence (EI) encompasses the ability to identify, understand, and manage emotions in oneself and others. It plays a critical role in workplace communication, enhancing interactions, and promoting collaboration. Research shows that leaders with high EI can improve their teams' performance by about 30%.
In a professional setting, having a high EI doesn't just mean being aware of your emotions but also tuning into the emotions of your colleagues. Recognizing these feelings can lead to better conflict resolution and foster a more inclusive environment. This awareness allows individuals to navigate complex interpersonal dynamics effectively.
Key Components of Effective Communication
- Active Listening
- Non-Verbal Cues
- Empathy
- Clear Messaging
Effective communication is rooted in several key components, notably Active Listening. This implies more than just hearing the words spoken; it requires engagement and thoughtful feedback. When team members feel heard, they are more likely to contribute ideas and support one another.
Furthermore, non-verbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice can significantly impact how messages are received. Being mindful of these signals can lead to more productive conversations and diminish misunderstandings.
Implementing Active Listening Techniques in the Office
Active listening can enhance workplace relationships and pave the way for more effective decision-making. Practicing techniques such as paraphrasing what the other person has said can demonstrate that you value their input.
Another strategy involves asking open-ended questions that invite further discussion. This approach not only shows your commitment to understanding the speaker but also encourages deeper engagement in conversations.
Using Non-Verbal Communication Effectively
Non-verbal communication can often convey more than spoken words. Awareness of your body language, eye contact, and even your personal space can significantly influence interactions. For instance, maintaining appropriate eye contact can portray confidence and attentiveness.
Additionally, mirroring the body language of others can establish rapport and create a sense of connection. This subconscious behavior often helps to foster an atmosphere of trust and openness in the office.
The Role of Empathy in Building Relationships
Empathy is the cornerstone of all effective communication in the workplace. By developing your capacity to empathize, you can not only cultivate stronger relationships but also enhance team dynamics. Observational studies indicate that teams with high levels of empathy tend to outperform those that lack it.
Practicing empathy involves seeing situations from another person’s perspective, which can lead to more thoughtful responses. When colleagues feel understood, their willingness to collaborate increases, resulting in an overall boost in morale and productivity.
Strategies for Clear and Concise Messaging
Clear messaging is critical in reducing confusion and ensuring everyone is on the same page. Make it a point to structure your communications effectively, using bullet points or numbered lists to highlight key information. This method can improve comprehension and retention, especially when discussing complex topics.
You might also consider tailoring your communication style to your audience. For instance, if you are addressing a technical team, using industry jargon may be appropriate; however, if conversing with non-technical stakeholders, simpler language can facilitate understanding.
Read more about Practical Tips for Improving Emotional Intelligence in the Office
Hot Recommendations
- Kayleigh McEnany: Profile, Career Highlights, and Media Influence
- Iron Fist: Marvel Series Review, Key Moments, and Fan Reactions
- Larry Ellison: Tech Mogul’s Legacy, Business Strategies, and Wealth Insights
- Marquette University: Campus Innovations, Academic Programs, and Student Life
- Flores Amarillas: Cultural Significance and Local Community Insights
- HBO Max: Streaming Updates, New Releases, and Subscription Benefits
- Sinkhole Route 287 Parsippany NJ: Infrastructure Challenges and Safety Updates
- Affordable Housing on Federal Lands: Policy Insights & Community Impact
- Nita Lowey: Political Legacy, Legislative Impact, and Career Retrospective
- Alex Verdugo: MLB Profile, Hitting Stats, and Career Highlights