Statue of Liberty Unveiled: History, Renovations & Visitor Tips
Outline
The Statue of Liberty was a gift from France, symbolizing friendship.
Construction began in 1875, completed in 1884, unveiled in 1886.
The statue represents freedom, democracy, and America’s welcoming spirit.
Renovations occurred to enhance structural integrity and visitor experience.
Visitors should reserve tickets in advance, especially during peak seasons.
The statue influences American culture, inspiring art and political discourse.
Ongoing preservation efforts ensure its longevity and historical significance.
Renovations improve visitor interaction and educational resources.
Advanced technologies aid in effective restoration and preservation processes.
Community engagement initiatives foster appreciation for the statue’s history.
Planning visits during off-peak times offers a better experience.
Comfortable shoes are essential for exploring Liberty Island.
Museum exhibits provide insights into the statue's historical context.
Audio tours enhance visitor understanding of the monument's significance.
Online resources allow access to virtual tours and digital materials.
Exhibits showcase the engineering marvel and history of the statue.
Accessibility features ensure all visitors can enjoy the monument.
Future initiatives aim to expand educational offerings and outreach.
Historical Insights into the Statue of Liberty
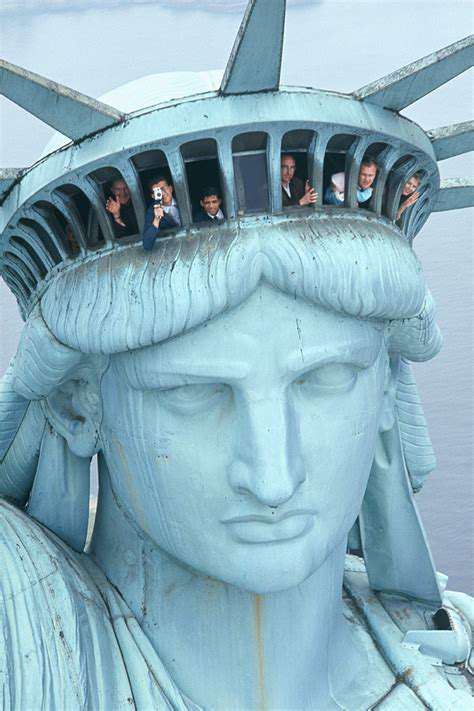

Origins and Construction of the Statue
The Statue of Liberty arrived as a transatlantic gesture of camaraderie from France, embodying shared revolutionary ideals. Crafted by Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi with Gustave Eiffel's engineering expertise, this colossus took 21 years from concept to completion. Workers hammered 300 copper sheets thinner than two pennies into shape before shipping 214 crates across the Atlantic in 1885.
Though conceived for America's 1876 centennial celebrations, funding shortages and logistical nightmares delayed the unveiling. When Lady Liberty finally emerged from her canvas shroud on October 28, 1886, fog horns blared across New York Harbor as dignitaries praised the triumph of Franco-American friendship.
Symbolism Woven into Bronze
More than mere metal, this monument pulses with layered meanings. The seven spikes on her crown don't just catch sunlight - they mirror the seven seas and continents, proclaiming liberty's universal reach. Her tablet bearing JULY IV MDCCLXXVI weighs 2,500 pounds, a concrete reminder of democracy's birth pangs.
Few notice the broken shackle beneath her drapery - a subtle nod to abolition that sparked heated debates during construction. This hidden detail transforms the statue into a palimpsest of American contradictions, inviting fresh interpretations with each generation.
Breathing New Life Through Restoration
- 1984-86 Centennial Restoration: 2,000 replaced rivets, new gold-leaf torch
- 2011-12 Hurricane Sandy Repairs: $30 million flood mitigation system
- 2023 Climate Resilience Upgrades: Corrosion-resistant alloy panels installed
The 1980s restoration revealed surprising truths - rain leakage had created miniature ecosystems inside the statue, with mineral deposits mimicking stalactites. Conservators used dental tools to clean delicate surfaces, blending art conservation with archaeological precision.
Modern restorers face new challenges: climate change accelerates copper oxidation, turning the statue's skin 30% thinner since 1886. Recent upgrades include smart sensors that track structural stresses in real-time, marrying preservation with cutting-edge tech.
Navigating the Modern Pilgrimage
Today's visitors encounter a carefully choreographed experience. Ferries now depart from three locations, but the Battery Park queue still snakes around sidewalks by 9 AM. Pro tip: The Jersey City departure offers shorter lines and stunning lower Manhattan vistas during the 20-minute crossing.
Crown access remains the ultimate prize - only 240 daily slots for climbing 354 narrow steps. Rangers chuckle about engagement rings left on the observation platform, dropped by overeager proposers reaching for pockets mid-knee.
Cultural Ripples Through Time
From Lazarus' famous sonnet to Ghostbusters II's climactic showdown, Lady Liberty permeates pop culture. During WWII, her torch went dark except for three days following D-Day - a silent protest against blackout regulations that moved thousands.
Immigrant oral histories reveal unexpected connections: a 1920s stowaway claimed the statue's torch guided his raft through fog, while 9/11 survivors describe using her silhouette to navigate dust-choked streets.
Preserving Tomorrow's Icon
Conservationists now wage war on microscopic threats. Preservation efforts include laser-cleaning patinas and 3D-printing replacement parts using original workshop blueprints. A recent breakthrough involves nanoparticle coatings that repel pollutants while letting the copper breathe naturally.
The statue's caretakers face philosophical dilemmas - how much modernization violates historical authenticity? Current protocols mandate visible differentiation between original and replacement materials, creating a visible timeline of American preservation ethics.
The Renovations that Preserved the Statue’s Legacy
Engineering Time Travel: 1986 Centennial Makeover
The statue's first major facelift became a crash course in Victorian engineering. Workers discovered 19th-century beer bottles left inside the armature - either accidental or the world's most ambitious time capsule. The torch replacement required custom-made 24k gold leaf sheets, each thinner than a human hair.
Unexpected challenges emerged: replacing the rusted armature demanded custom-forged stainless steel bars that could flex with wind sway. The solution? A hybrid system using Eiffel's original puddle iron where possible, seamlessly integrated with modern alloys.
Digital Guardians: Tech-Driven Conservation
Today's preservationists wield terabyte-sized tools. Drones equipped with multispectral cameras map corrosion patterns invisible to the naked eye, while AI algorithms predict stress points years before failures occur. The statue now has its own digital twin - a millimeter-perfect 3D model updated annually to track micro-changes.
Grassroots Guardianship Initiatives
Local schools now adopt sections of the statue through the Community Engagement program. Third-graders track patina changes using classroom microscopes, while high schoolers compete to design sustainable preservation solutions. This fall, a teen's graphene coating concept will undergo field testing.
The Living History program trains immigrants as tour guides, weaving personal narratives with historical facts. A recent Syrian refugee's account of seeing the statue from a rescue ship brought tears to visitors' eyes, bridging past and present struggles for freedom.
Visiting the Statue of Liberty: Essential Tips for an Enjoyable Experience
Timing is Everything
For photographers, the blue hour - 30 minutes after sunset - transforms the statue into a silhouette against candy-colored skies. Winter visits offer magical frost-tinged views, though the crown closes when temperatures dip below 20°F.
Ticket Hacks
Local secret: The CityPASS includes statue access plus five other attractions, saving 40% compared to individual tickets. Military families should ask about free National Park passes at the ticket booth.
Unexpected Delights
Few know about the secret ranger-led Hard Hat Tour that explores the statue's infrastructure. Offered sporadically, this 3-hour deep dive requires advance booking and sturdy knees for ladder climbing.
Hidden History Spots
Behind the museum lies the original 1886 torch - weathered but majestic. Run your fingers along its copper surface to feel century-old hammer marks from Parisian artisans.
Educational Resources Available at the Statue of Liberty

Immersive Learning Labs
The new Educational Materials and Interactive Exhibits include a wind tunnel simulator showing how the statue sways up to 3 inches in storms. Visitors can try assembling virtual copper panels using 19th-century tools - spoiler alert, it's harder than it looks!
Augmented Reality Explorations
Download the official app to see archival photos superimposed on your camera view. Watch 1886 spectators materialize around you in top hats, or see the original torch flame flicker in augmented reality.
Culinary History Tours
New food-themed walks explore the statue's forgotten kitchen history. Learn how workers survived on baguettes and vin ordinaire during construction, then sample recreated 1880s lunch pails at the café.
Preservation Workshops
Monthly hands-on sessions teach copper-smithing techniques using replica tools. Participants leave with their own miniature Liberty torch - perfect for inspiring future conservators.
Read more about Statue of Liberty Unveiled: History, Renovations & Visitor Tips
Hot Recommendations
- Duke Basketball: A Legacy of Excellence – Season Recap and Future Stars
- One Battle After Another: Stories of Overcoming Challenges and Triumphs
- MLB Games Tonight: Schedule, Scores & Key Matchups to Watch
- Men’s March Madness 2025: Expert NCAA Bracket Predictions & Winning Strategies
- Spring Equinox 2025 Celebrations: History, Traditions, and How to Enjoy the Day
- Trump’s Education Policies: What the Department of Education Means for 2025
- First Day of Spring 2025: Seasonal Traditions, Celebrations & Outdoor Tips
- Bulls vs Kings: In Depth NBA Game Analysis and Key Player Stats
- The Rise of Jordan Mason: Career Highlights and Future Prospects
- Hudson River: Environmental Insights, History & Scenic Exploration