Oil Rich Peninsula: Analyzing the NYT Report and Global Economic Impact

Examining the NYT's Reporting on the Recent Economic Crisis
The New York Times has consistently provided in-depth coverage of the recent economic downturn, offering a valuable resource for understanding the multifaceted nature of the crisis. Their reporting often delves into the intricacies of government policies, exploring how these measures are impacting businesses, consumers, and the overall economic landscape. This comprehensive approach allows readers to gain a nuanced perspective on the challenges and opportunities arising from this period.
A critical aspect of the NYT's reports is their focus on the human element of the crisis. They skillfully intertwine economic data with personal stories of individuals and families affected by job losses, decreased income, and the overall uncertainty surrounding their financial futures.
Analyzing the Impact of Government Policies
The NYT's articles have meticulously analyzed the various government interventions implemented to mitigate the economic fallout. This includes examining the efficacy of stimulus packages, the effectiveness of bailouts, and the broader consequences of these actions on different sectors of the economy. These analyses often contrast the intended effects with the actual outcomes, offering a critical lens through which to view policy decisions.
The reporters also investigate the potential long-term ramifications of these interventions, examining factors such as inflation, debt levels, and future economic growth prospects. The thoroughness of these analyses is a key strength of the NYT's reporting.
Evaluating the Role of Global Markets
The NYT provides valuable insights into the interconnectedness of global markets, highlighting how events in one part of the world can quickly ripple across borders. Their reporting frequently explores the global supply chain, demonstrating how disruptions in one region can impact production and distribution across the entire planet. This global perspective is essential for understanding the complexity of economic challenges.
International trade, currency fluctuations, and political instability are all thoroughly examined by the NYT. These factors contribute to the broader economic narrative and the complex interactions between various economies, providing a well-rounded perspective.
Investigating the Response from Businesses and Corporations
The New York Times' coverage often features insightful examinations of the strategies adopted by businesses and corporations in response to the economic downturn. Their reporting scrutinizes mergers and acquisitions, divestitures, and overall corporate restructuring, providing a nuanced perspective on how these actions are shaping the business landscape.
The reports also analyze the impacts of changing consumer behavior and market trends on these organizations. By combining financial data with an understanding of corporate dynamics, the NYT brings a unique and valuable perspective to the economic narrative.
Assessing the Long-Term Implications of the Crisis
The NYT's ongoing coverage of the recent economic downturn also delves into the long-term ramifications of the crisis. They look at potential societal impacts, economic shifts, and structural changes in the way that economies operate around the world. This forward-thinking approach contributes significantly to a deeper understanding of the unfolding crisis.
Forecasting future trends and identifying potential challenges are key aspects of this type of reporting. This insight is crucial for stakeholders and individuals as they prepare for the complexities of the future economic landscape. By considering these factors, the NYT provides valuable information to navigate the challenges ahead.
Impact on Global Energy Markets: A Shifting Landscape
The Geopolitical Implications of Production Changes
The recent fluctuations in oil production from the oil-rich peninsula have sent ripples through global energy markets, triggering a complex interplay of geopolitical factors. The decisions made by the producing nations, influenced by internal political dynamics, international relations, and economic pressures, have a direct impact on the global energy supply chain. This instability creates uncertainty for consumers and businesses, leading to price volatility and adjustments in energy procurement strategies. Understanding these complex interactions is crucial for predicting and mitigating potential disruptions in the global energy landscape, which can affect everything from transportation costs to industrial production.
Further complicating the situation are international alliances and rivalries. The actions of one nation in the oil-rich peninsula can have unforeseen consequences for others, potentially leading to increased tensions or unexpected collaborations. This complex web of relationships makes it challenging to isolate the precise impact of each decision, requiring a comprehensive understanding of the political and economic landscape to properly assess the shifting geopolitical climate. The long-term effects of these production changes on international relations remain to be seen, and their implications will continue to be closely watched as the energy markets evolve.
Economic Consequences of Supply Shifts
The shifting landscape in global energy markets due to production changes in the oil-rich peninsula has significant economic ramifications. Changes in oil production directly affect the prices of oil and related energy products, impacting everything from transportation costs and consumer prices to the profitability of industries that rely heavily on oil as a raw material. The ripple effect of these price fluctuations is felt throughout the global economy, triggering adjustments in supply chains and potentially affecting international trade relations. This intricate web of economic consequences makes it essential to analyze the financial implications of these production shifts, which often create uncertainties in investment decisions and economic forecasting.
Furthermore, the volatile energy market can impact global inflation rates, leading to broader economic uncertainties. Businesses and consumers alike face challenges in adapting to price volatility and uncertainty, which can have substantial effects on employment, investment and economic growth. A deeper understanding of the economic consequences of supply-side changes in the oil-rich peninsula will help develop strategies to mitigate the impacts and maintain a stable global economy, particularly for those nations highly reliant on imported energy.
The ongoing influence of the oil-rich peninsula on global energy markets underscores the importance of understanding the interconnectedness of global economies and the critical role energy plays in driving economic activity and shaping geopolitical dynamics. Evaluating the short-term and long-term impacts on the global economy and consumer confidence is paramount, offering insights into potential policy adjustments and future trends.
Economic Fallout: Regional and Global Consequences
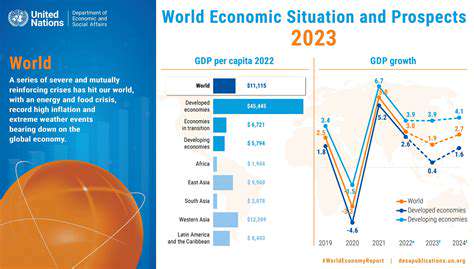
Economic Downturn Impacts
The recent economic downturn has had a significant ripple effect across various sectors, leading to job losses, reduced consumer spending, and a decline in overall economic activity. This downturn is particularly acute in regions heavily reliant on specific industries, such as manufacturing or tourism. The resulting unemployment and decreased purchasing power have further hampered regional economic growth, impacting local businesses and creating a cycle of hardship.
These economic challenges are not isolated incidents but rather manifestations of broader systemic issues. The interconnected nature of modern economies means that a downturn in one region can quickly cascade to others, requiring coordinated responses to mitigate the negative impacts.
Regional Unemployment Rates
Analyzing regional unemployment rates reveals stark disparities across the affected areas. Certain regions have experienced double-digit unemployment, particularly those heavily concentrated in industries facing decline or restructuring. This high unemployment not only impacts individuals but also strains social safety nets and public resources, requiring substantial government intervention to address the immediate needs and longer-term solutions.
Furthermore, the rising unemployment rates contribute to a decline in household income and consumer confidence. This, in turn, further dampens economic activity, creating a challenging economic environment for businesses to navigate.
Impact on Small Businesses
Small businesses, the backbone of many communities, are disproportionately affected by economic downturns. Reduced consumer spending directly impacts their revenue streams, leading to decreased profitability and, in some cases, closure. These closures have devastating consequences, leading to job losses and a decrease in local economic vitality.
The loss of these small businesses also results in the loss of important local services and innovation, which weakens the overall regional economy. Efforts to support small businesses during downturns are critical for maintaining the fabric of local communities.
Global Supply Chain Disruptions
The global supply chain disruptions caused by the current economic challenges have complicated the situation for numerous regions. Businesses face increased costs and delays in sourcing materials and fulfilling orders, which directly impacts profitability. These disruptions further compound the negative effects on regional economies, necessitating strategies for enhanced resilience.
These disruptions are also impacting the availability of essential goods and services, potentially leading to shortages and price increases, which negatively impact households and businesses.
Government Response and Policies
Governments worldwide have been implementing various economic stimulus packages and policies to mitigate the effects of the downturn. These policies aim to boost economic activity, provide support to businesses, and safeguard vulnerable populations. It remains vital to carefully assess these interventions and their potential long-term impact on regional economies.
The long-term effectiveness of these policies will depend on their ability to address the root causes of the downturn, foster innovation, and promote sustainable economic growth.
Infrastructure and Investment
Regional economic development often hinges on investments in infrastructure, such as transportation networks, communication systems, and essential utilities. Robust infrastructure is essential for attracting businesses, facilitating trade, and boosting economic productivity. Investments in these areas can provide a much-needed boost to the economy and stimulate job creation.
Prioritizing infrastructure development can not only improve current economic conditions but also prepare regions for future challenges and opportunities.
Read more about Oil Rich Peninsula: Analyzing the NYT Report and Global Economic Impact
Hot Recommendations
- Hawks vs Hornets: NBA Game Preview, Key Players & Tactical Analysis
- Tornado Watch vs Warning: What’s the Difference and How to Stay Safe
- Alexandra Daddario: Hollywood Career, Iconic Roles & Upcoming Projects
- Wombats in Australia: Fascinating Facts, Conservation Efforts & Where to See Them
- St. Patrick’s Day 2025: History, Festivities & Modern Celebrations
- Fabian Schmidt: Profile, Career Impact & Notable Achievements
- Alex Consani: Profile, Career Highlights, and Notable Achievements
- Vivian Wilson: Profile, Career Milestones & What’s Next
- Harriet Hageman: Political Profile and Impact on National Policy
- Bryant University Basketball: Rising Stars and Season Highlights
